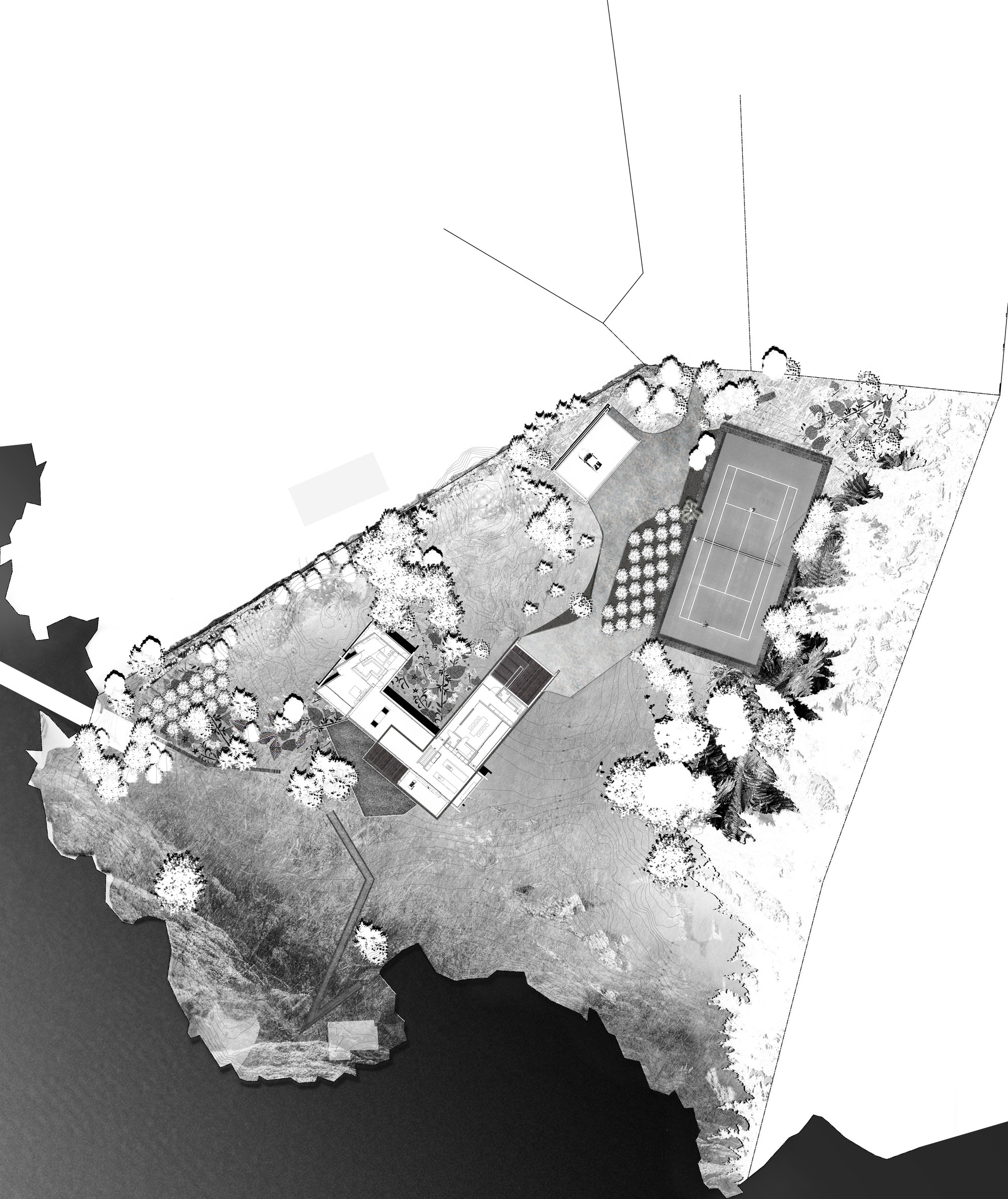
Architectural site analysis involves a thorough examination and evaluation of a potential construction site to gather vital information. This assessment enables architects and designers to make informed decisions based on the site’s characteristics, limitations, and opportunities. By conducting a comprehensive site analysis, we can uncover valuable insights that influence the design process, construction techniques, and overall project feasibility.
Factors Considered in Site Analysis
- Site Location: Evaluating the location of a construction site is crucial. Factors such as accessibility, proximity to amenities, transportation routes, and surrounding infrastructure are carefully analyzed.
- Topography and Geology: The physical features and geological composition of a site significantly impact architectural design and construction methods. Understanding the topography helps us determine the best utilization of the land and identify any potential challenges or advantages.
- Climate and Microclimate: Examining the climate conditions of a site allows us to incorporate sustainable design principles. By considering factors such as sunlight exposure, wind patterns, and precipitation levels, we can optimize energy efficiency and create comfortable living or working environments.
- Environmental Considerations: We conduct an environmental assessment to identify any ecological sensitivities or potential impacts on the surrounding ecosystem. This information guides us in designing projects that align with sustainable practices and minimize ecological disturbances.
- Legal and Regulatory Factors: Understanding the local zoning regulations, building codes, and legal requirements is paramount in ensuring compliance and avoiding future complications. By conducting a site analysis, we can proactively address any legal or regulatory constraints.
Mermaid Diagram: Architectural Site Analysis Overview
graph TD
A[Site Analysis]
A –> B[Site Location]
A –> C[Topography and Geology]
A –> D[Climate and Microclimate]
A –> E[Environmental Considerations]
A –> F[Legal and Regulatory Factors]
The Significance of Feasibility Studies
Feasibility studies are comprehensive assessments conducted to determine the viability and potential success of a construction project. They involve in-depth analyses of various factors, providing invaluable insights into the project’s financial, technical, and operational aspects. By undertaking a thorough feasibility study, we can mitigate risks, optimize resource allocation, and ensure the project’s overall viability.
Key Aspects of Feasibility Studies
- Market Analysis: Understanding the market dynamics, demand, and potential competition is vital to evaluate the project’s viability. This analysis helps identify the target audience, assess market trends, and determine the project’s potential profitability.
- Financial Assessment: Conducting a financial analysis enables us to evaluate the project’s financial feasibility. We consider factors such as budgeting, cost estimation, cash flow projections, and potential return on investment. This information helps stakeholders make informed decisions regarding project funding and financial viability.
- Technical Evaluation: A technical evaluation examines the project’s technical requirements, including architectural design, engineering considerations, materials, and construction methods. This assessment ensures that the project aligns with technical standards and identifies any potential challenges or opportunities.
- Risk Analysis: Assessing and mitigating risks is essential to minimize project uncertainties and increase the likelihood of success. Feasibility studies identify potential risks, such as market fluctuations, regulatory changes, or unforeseen challenges, enabling proactive risk management strategies.
- Operational Considerations: Understanding the operational requirements of a project is crucial for its successful implementation. This includes evaluating staffing needs, logistical considerations, and operational processes. By conducting a thorough feasibility study, we can identify any operational bottlenecks and develop strategies for smooth project execution.
Mermaid Diagram: Feasibility Study Process
graph TD
A[Feasibility Study]
A –> B[Market Analysis]
A –> C[Financial Assessment]
A –> D[Technical Evaluation]
A –> E[Risk Analysis]
A –> F[Operational Considerations]
FAQ’s
1. What is Master Planning in Site Feasibility and the Importance of Master Planning in Architecture?
In architecture, a master plan is a blueprint or set of drawings created at the beginning of a project that serves as a detailed, long-term guideline for the entire undertaking. A master plan is developed based on the findings of feasibility studies. It defines the key components of the project, provides information about the surrounding areas, identifies different spaces within the project, determines the building’s height, involves stakeholders, and identifies opportunities and challenges related to the site. A well-thought-out master plan can provide direction to the project, optimize space utilization, and save the client money. Additionally, a master plan enables budgeting and cost estimation at the start of the project, ensuring quicker completion.
2. How Do I Create a Master Plan for My Site?
To create a master plan for your site, you need to perform a feasibility study and understand the topography and environmental factors of the location. Then, you can incorporate the distinct features of the site into three-dimensional models and calculate the carpet area, built-up area, and floor area ratio (FAR).
3. Why Are Floor Area Ratio, Built-Up Area, and Coverage Essential to Master Planning?
Floor area ratio, built-up area, and coverage are essential to master planning because they determine the permissible limits for construction within a city or area. Each location has assigned spaces for construction as defined by governing authorities, and buildings must comply with these limits. The built-up area is necessary for calculating the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) or Floor Space Index (FSI).
FAR is a crucial metric used to ensure that construction does not exceed the designated area and complies with zoning regulations. Architects calculate the built-up area, FAR, and building coverage ratio to facilitate cost estimation and land use planning. These calculations also help determine rental or apartment selling rates, making accuracy essential to avoid costly errors for clients.
4. How Do I Calculate Carpet Area, Floor Area Ratio, Built-Up Area, and Coverage?
Carpet area represents the usable area within an apartment, excluding the thickness of the walls. If you were to spread a carpet from one inner wall to another, you would measure the carpet area. Areas outside the apartment, such as lobbies and terraces, are not included in the carpet area.
Built-up area refers to the carpet area plus the areas covered by internal and external walls. It generally accounts for approximately 10-15% more than the carpet area and includes balconies, terraces, lobbies, and other relevant spaces.
Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is calculated by dividing the total covered area of all floors in a building by the total area of the plot. For instance, if you have a 1,000 square feet plot and the FSI in the area is 1.8, you can construct up to 1,800 square feet of covered structures on that land.
5. How Do You Determine the Number of Floors a Building Can Have?
The number of floors a building can have is determined by the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) guidelines. Architects must also consider the minimum setback requirements set by governing bodies while planning the building’s height and floors.
6. What is Zoning Analysis in Architectural Feasibility Study?
Zoning analysis is an essential part of the architectural feasibility study. Local governing bodies establish zoning regulations that define the permitted use of space, such as residential, commercial, or mixed-use purposes. Zoning regulations cover aspects like building size, height, FAR, permissible floors, and setbacks. Architects perform zoning analysis during the site feasibility study to determine what can be developed according to the applicable zoning codes. Architects need to conduct zoning analysis to ensure compliance with these regulations before proposing a plan.
6. What is Zoning Analysis in Architectural Feasibility Study?
Zoning analysis is an essential part of the architectural feasibility study. Local governing bodies establish zoning regulations that define the permitted use of space, such as residential, commercial, or mixed-use purposes. Zoning regulations cover aspects like building size, height, FAR, permissible floors, and setbacks. Architects perform zoning analysis during the site feasibility study to determine what can be developed according to the applicable zoning codes. Architects need to conduct zoning analysis to ensure compliance with these regulations before proposing a plan.